4.23 TERMINAL
TERMINAL constructs an object to represent equipment that transfers energy to or from the current zone from a local heating device (coil, etc.) and/or one AIRHANDLER. A terminal serves a zone (and, internally, is owned by a zone). Up to three terminals can be defined for each zone.
A terminal can have local heating capability, using a simulated reheat coil, baseboard heater, etc. and/or air heating/cooling capability, using a simulated variable air volume (VAV) box connected to an AIRHANDLER (Section 0). Since a TERMINAL can only connect to a single air handler, use two terminals per zone to model systems where separate air handlers supply hot and cool air (dual duct). If a local heat capability utilizes the air flow (e.g. a reheat coil), model it in the terminal connected to the air handler; if a local heat capability is independent of air flow (e.g. electric baseboard heaters), it doesn’t matter whether you model it with a separate terminal.
Each capability can be set output, in which the output is constant or determined by external conditions such as in an outdoor reset baseboard situation or set temperature, in which the output is modulated to maintain the zone temperature at a set point. Set temperature operation is established by giving the setpoint for the capability (tuTLh, tuTH, tuTC); set output operation is established by specifying the local heat output (tuQMnLh) or air flow (tuVfMn) without specifying a setpoint.
Hourly variable expressions may be used as desired to schedule setpoints and flow limits. Figure 1 shows [need sentence describing the figure.]
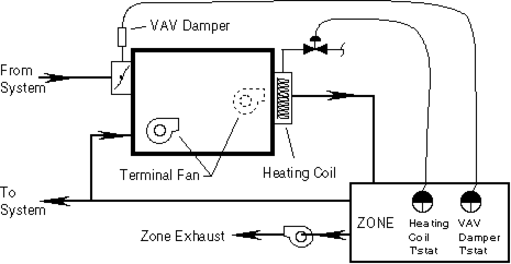
tuName
Optional name of terminal; follows the word “TERMINAL” if given.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 63 characters | No | constant |
4.23.1 TERMINAL Local Heating
These commands establish the TERMINAL’s local heating capability and determine whether it operates in set output or set temperature fashion. Additional details of the local heating mechanism are given with commands described below under terminal heating coil.
Either tuTLh or tuQMnLh must be given to establish the TERMINAL’s local heat capability:
tuTLh=float
Local heating thermostat setpoint. Hourly expression may be used to schedule as desired. Giving this implies set temperature local heat from this terminal; omitting implies no local heat or, if tuQMnLh is given, set output local heat.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| oF | x \(>\) 0 | no thermostat control | No | hourly |
tuQMnLh=float
Minimum local heat output or set local heat output. If tuTLh is given, this is the minimum output, used when the thermostat is not calling for (local) heat. If tuTLh is not given, giving tuQMnLh implies set output local heat and specifies the set output level. An hourly expression may be used to schedule as desired.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Btuh | x \(\ge\) 0 | 0 if tuTLh given else no local heat | For set output local heat | hourly |
The next three items are allowed only for thermostat controlled local heating (tuTLh given):
tuQMxLh=float
Maximum desired power, used when thermostat is calling for heat continuously, subject to coil capacity, and to HEATPLANT limitations where pertinent (see tuhcCaptRat description). If tuQMxLh is less than minimum power (tuQMnLh), the latter is used, effectively disabling setpoint control.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Btuh | x \(\ge\) 0 | Yes, if tuTLh given | hourly |
tuPriLh=int
Setpoint priority: when there is more than one capability with the same setpoint, that with the highest priority (lowest value) is used first. The defaults for tuPriLh (100) and tuPriH (1) cause maximum air heat to be used before local heat, if both are present and the setpoints are the same. Two or more equal setpoints with equal priorities in the ZONE cause an error, even if in different TERMINALs.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x \(>\) 0 | 100 | No | constant |
tuLhNeedsFlow=choice
| YES | local heat being modeled requires terminal air flow (e.g. reheat coil). Local heat is then disabled when there is zero air flow through the terminal (when simulated VAV damper set to 0 flow, or when air handler fan and terminal fan both off) |
| NO | no local heat or does not require air flow (e.g. baseboard heaters). |
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YES, NO | NO | No | constant |
4.23.2 TERMINAL Air Heating and Cooling
These commands establish whether the TERMINAL has air capability (heat, cool, or both), and whether the capability operates in set temperature mode (tuTH and/or tuTLh given) or set output mode (tuVfMn given without tuTH and tuTLh). They further establish the setpoints, flow limits, leakages, and losses.
Caution should be exercised in using air heat and air cooling in the same terminal. The supply air for both comes from the same air handler; it is up to you to make sure the terminal only calls for heat when the air handler is blowing hot air and only calls for cooling when the air handler is blowing cold air. This is done by carefully coordinating the variable expressions for terminal air heating and cooling setpoints (tuTH and tuTC here) and the air handler supply temperature setpoint (AIRHANDLER ahTsSp, Section 0).
Note: To autosize air flows for a constant volume terminal, use the following
AUTOSIZE tuVfMxC
AUTOSIZE tuVfMxH
AUTOSIZE tuVfMn
tuVfMxHC = SAMEtuAh=ahName
Name of air handler supplying this terminal.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name of an AIRHANDLER | If omitted, terminal has no air heating nor cooling capability. | No | constant |
If both of the following (tuTH and tuTC) are specified, be careful not to accidentally permit the heating setpoint to be active when the air handler is blowing cold air, or vice versa. CSE’s simulated thermostats and VAV boxes are at least as dumb as their real counterparts; if the thermostat calls for heat, the VAV damper will open even if the supply air is colder than the zone. To schedule deactivation of the air heating or cooling capability, schedule an extreme setpoint, such as 1 for heating or 199 for cooling.
Giving neither tuTH nor tuTC implies that the terminal has no set temperature air capability; it will then have set output air capability if tuVfMn is given.
tuTH=float
Air heating thermostat set point; implies set temperature air capability. May be scheduled as desired with an hourly expression; to disable set temperature operation at certain times (as when air handler is scheduled to supply cold air), schedule a low temperature such as 1.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | **Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| oF | x \(\ge\) 0 | No thermostat-controlled air heating | No | hourly |
tuTC=float
Air cooling thermostat set point; implies set temperature air capability. May be scheduled as desired; to disable at certain times, schedule an extreme temperature such as 199.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | **Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| oF | x \(\ge\) 0 | No thermostat-controlled air cooling | No | hourly |
tuVfDs=float
Design air flow rate. (“Vf” in member names stands for “Volumetric Flow”, to emphasize that flow is specified by volume at actual air temperature (cfm), not by mass (lb/hr), nor heat capacity (Btuh/F), etc.)
The design air flow rate is used to apportion the available cfm among the terminals when the total flow demand of the terminals exceeds the air handler’s supply fan capacity; it is unimportant (but may nevertheless be required) if the total of the tuVfMx’s of the terminals on the air handler is not greater than the air handler’s fan capacity including overrun.
CSE will default tuVfDs to the largest of tuVfMn, tuVfMxH, and tuVfMxC unless a variable expression is given for any of them. Thus, you must given tuVfDs only when a variable minimum or maximum flow is used, or when you wish to override the default cfm apportionment under fan overload conditions.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cfm | x \(\ge\) 0 | largest of tuVfMn, tuVfMxH, and tuVfMxC if all are constant | Yes, if tuVfmn, tuVfmxH, or tuVfMxC is variable | hourly |
tuFxVfHC=float
Sizing factor for autosized terminal air flows. Default value (1.1) specifies 10% oversizing.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x \(\ge\) 0 | 1.1 | No | constant |
tuVfMxHC=choice
Determines autosizing strategy for heating and cooling air flows.
| SAME | tuVfMxH and tuVfMxC are set to the larger of the autosized values |
| DIFFERENT | tuVfMxH and tuVfMxC are autosized independently |
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| choices above | Different | No | constant |
tuVfMn=float
Minimum terminal air flow rate or set output air flow rate. An hourly expression may be used to schedule the minimum or set output flow as desired.
If neither tuTH nor tuTC is given, giving tuVfMn implies set output air capability for the terminal; the tvVfMn value is the set output cfm.
If either setpoint (tuTH or tuTC) is given, tuVfMn is the cfm used when the thermostat is not calling for heat nor cold; it might be non-0, for example, to meet ventilation requirements. If tuVfMn is larger than tuVfMxH (when heating) or tuVfMxC (when cooling), it overrules them; thus a minimum (e.g. ventilation) requirement need not be considered in formulating expressions for the maximum flows.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cfm | AUTOSIZE or x \(\ge\) 0 | if tuTH or tuTC given, else no air heat/cool | For set output air operation | hourly |
tuVfMxH=float
Maximum heating air flow rate, subject to air handler limitations. This terminal flow is used when the thermostat is calling for heat continuously. Hourly schedulable. If not greater than tuVfMn, the latter flow is used, thus disabling thermostat control.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cfm | AUTOSIZE or x \(\ge\) 0 | none | If tuTH given | hourly |
tuVfMxC=float
Maximum cooling air flow rate, before air handler limitations, used when the thermostat is calling for cooling continuously. tuVfMn overrides if larger.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cfm | AUTOSIZE or x \(\ge\) 0 | none | If tuTC given | hourly |
tuPriC=int
Cool setpoint priority. The lowest numbered priority is used first when there are equal setpoints in a zone; equal heat or cool setpoints with equal priority in same ZONE (even if on different TERMINALs) constitute an error.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x \(>\) 0 | 1 | No | constant |
tuPriH=int
Heat setpoint priority. Lowest numbered priority is used first when there are equal setpoints in a zone. Default for tuPriLh is larger, so that by default local heat is not used unless maximum air heat is insufficient, when both local heat and air heat are present in zone and have same setpoint.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x \(>\) 0 | 1 | No | constant |
tuSRLeak=float
Leakage of supply air to return, increasing supply volume and return temperature. Note that this is a fraction of current cfm, whereas air handler leak (before VAV dampers) is a fraction of maximum cfm. TfanOffLeak is added to this if terminal has a fan that is not running (future, 7-92).
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 \(\le\) x \(\le\) 1 | 0.05 | No | constant |
tuSRLoss=float
Supply air to return plenum heat loss as a fraction of supply air to return air temperature difference. Not allowed if return is ducted (no plenum).
NOT IMPLEMENTED as of July 1992 – Plenums are unimplemented.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 \(\le\) x \(\le\) 1 | 0.1 | No | constant |
4.23.3 TERMINAL Heating Coil
These members are disallowed if terminal has no local heating capability, that is, if neither tuTLh nor tuQMnLh is given.
tuhcType=choice
Local heating coil type:
| ELECTRIC | Electric coil or heater, including separate heaters such as electric baseboards. 100% efficient; rated capacity always available. |
| HW | Hot water coil, using hot water from amHEATPLANT. Available capacity may be limited by HEATPLANT total capacity as well as by coil rated capacity. |
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELECTRIC (future: HW) | ELECTRIC, or NONE if no local heat | No | constant |
tuhcCaptRat=float
Rated capacity of the heating coil. The coil will never supply more heat than its capacity, even if tuQMxLh and/or tuQMnLh is greater. For an ELECTRIC coil, the capacity is always the rated capacity. For an HW coil, the capacity is the rated capacity when the HEATPLANT can supply it; when the total heat demanded from the HEATPLANT by all the HW coils in TERMINALs and AIRHANDLERs exceeds the HEATPLANT’s capacity, CSE reduces the capacities of all HW coils proportionately until the plant is not overloaded.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Btu/hr | AUTOSIZE or x \(\gt\) 0 | none | Yes | constant |
tuhcFxCap=float
Capacity factor for autosized terminal heating coil. Default value (1.1) specifies 10% oversizing.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x \(\ge\) 0 | 1.1 | No | constant |
tuhcMtr=mtrName
Name of meter, if any, which accumulates input energy for this coil. End use category used is “Htg”. Not allowed when tuhcType is HW, as the energy for an HW coil comes through a HEATPLANT; the input energy is accumulated to a meter by the HEATPLANT.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name of a METER | not recorded | No | constant |
tuhcHeatplant=heatplantName
Name of HEATPLANT for HW coil; disallowed for other coil types.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name of a HEATPLANT | none | If tuhcType is HW | constant |
4.23.4 TERMINAL Fan
Presence of a terminal fan is indicated by specifying a tfanType value other than NONE.
Terminal fans are NOT IMPLEMENTED as of July 1992.
tfanType=choice
Choice of:
| NONE | No fan in this TERMINAL (default); input for other terminal fan members disallowed. |
| SERIES | Fan runs whenever scheduled ON (see tfanSched, next); if VAV cfm < terminal fan cfm (tfanVfDs), the additional flow comes from the return air. |
| PARALLEL | Fan runs when scheduled ON (see tfanSched) and terminal’s simulated VAV cfm is less than tfanVfDs plus tuVfMn ?? plus tuVfMn??. Terminal fan cfm is added to VAV cfm from AIRHANDLER to get cfm to ZONE. |
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NONE, SERIES, PARALLEL | none | Yes, if fan present | constant |
tfanSched=choice
Terminal fan schedule. May be scheduled with an hourly variable expression.
| OFF | fan does not run |
| ON | fan may run |
| HEATING | fan may run when local heat is in use |
| VAV | fan may run when AIRHANDLER supply fan is on or when doing setback headting and ssCtrl is ZONE_HEAT or BOTH (future). |
A series fan (see tfanType) runs whenever on; a parallel fan runs only enough to keep terminal cfm at terminal minimum plus fan cfm; thus it may not run at all when the VAV flow from the AIRHANDLER is sufficient.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OFF, ON, HEATING, VAV | none | Yes (if fan present) | hourly |
tfanOffLeak=float
Backdraft leakage when terminal fan off., as a fraction of tfanVfDs.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 \(\le\) x \(\le\) 1 | 0.1 if fan present | No | constant |
tfanVfDs=float
Terminal fan design flow rate. To specify .x times zone or terminal cfm, use a CSE expression.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cfm | x \(\le\) 0 | none | Yes (if fan present) | constant |
tfanPress=float
Terminal fan external static pressure.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| inches H2O | x \(\ge\) 0 | 0.3 | No | constant |
tfanEff=float
Terminal fan/motor/drive combined efficiency.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 \(le\) x \(le\) 1 | 0.08 | No | constant |
tfanCurvePy=k0, k1, k2, k3, x0
k0 through k3 are the coefficients of a cubic polynomial for the curve relating fan relative energy consumption to relative air flow above the minimum flow x0. Up to five floats may be given, separated by commas. 0 is used for any omitted trailing values. The values are used as follows:
\[z = k_0 + k_1 \cdot (x - x_0)| + k_2 \cdot (x - x_0)|^2 + k_3 \cdot (x - x_0)|^3\]
where:
- \(x\) is the relative fan air flow (as fraction of tfanVfDs; 0 \(\le\) x \(\le\) 1);
- \(x_0\) is the minimum relative air flow (default 0);
- \((x - x_0)|\) is the “positive difference”, i.e. \((x - x_0)\) if \(x > x_0\); else 0;
- \(z\) is the relative energy consumption.
If \(z\) is not 1.0 for \(x\) = 1.0, a warning message is displayed and the coefficients are normalized by dividing by the polynomial’s value for \(x\) = 1.0.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 (linear) | No | constant |
tfanMtr=mtrName
Name of meter, if any, which is to record energy used by this terminal fan. The “fans” category is used.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name of a METER | not recorded | No | constant |
endTerminal
Optional to indicates the end of terminal definition. Alternatively, the end of the door definition can be indicated by END or by beginning another object.
| Units | Legal Range | Default | Required | Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x \(\ge\) 0 | none | No | constant |
Related Probes: